Install OpenHIM
Install Core and Console#
Once we have all our prerequisites completed we are now ready to spin up our OpenHIM instance using Docker. Open up a new terminal window and ensure that you are within the directory where the docker-compose.yml file is located and execute the below command:
Note: the user executing the above command will need to be an administrator for the docker-compose script to run successfully
The first time this command is run it will take some time to complete. This is because the Docker Compose file needs to pull the relevant images from Dockerhub that don't exist on your local machine. The Docker images will then be used to build the docker containers for our OpenHIM instance.
Once the docker-compose has successfully completed, you should see something like the below printed within your terminal. This means that the relevant images have been downloaded and the docker containers have been created.
Congratulations! :)#
Your OpenHIM instance has been successfully installed on your local machine. To view the OpenHIM instance we can navigate to http://localhost:9000
First time login#
Once your OpenHIM instance has successfully been created and you are able to access it on the above URL, you will need to login with the root user and reset the password. Supply the below root user details to continue with the installation process.
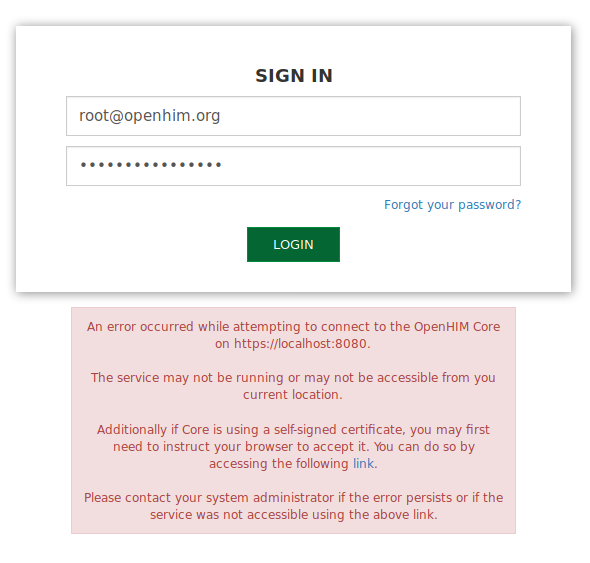
Important! If you are presented with a red information box when submitting the default
rootusers details, it means that you are using a self signed certificate that will need to be accepted by the browser first. Click on the link that is presented which will try and access the API heartbeat. The browser will present you with a security risk page to notify you of the self signed certificate. Depending on the browser you are using, click on theadvancedbutton and proceed to accept the un-trusted certificate so that we are able to successfully communicate with the OpenHIM core API
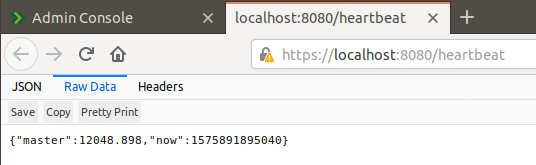
Once the self signed certificate has been accepted, or a valid certificate is being used for the OpenHIM core, you should see the below JSON output when viewing the /heartbeat endpoint within the OpenHIM core API. You are now able to proceed with successfully logging into the OpenHIM console
Useful Docker commands#
Below are a few useful Docker commands that will allow you to have better visibility into your OpenHIM/Docker setup
Check running processes#
Now that we have our OpenHIM successfully created and running, we might need to check up on our Docker processes running to find some additional metadata on our containers. Execute the below command to find all the running Docker processes.
Access the Openhim core logs#
To access the OpenHIM core logs, execute the below command within your terminal to see and follow (-f) the output of the container logs
Stop the Docker service#
To stop all the running OpenHIM Docker services, we need to execute the below command